With every webpage loaded, email sent, or video streamed, network traffic takes a complex journey…
Microsoft Teams has emerged as a vital communication and collaboration platform for modern workplaces. As organizations increasingly rely on Teams to conduct meetings, share files, and collaborate on projects, ensuring a seamless user experience becomes paramount. To achieve this, the implementation of effective Quality of Service (QoS) measures is crucial. In this article, we explore the significance of Teams QoS and delve into the technical aspects of its implementation, optimizing for enhanced Microsoft Teams monitoring with CloudReady and Service Watch.
Understanding Teams Quality of Service
Teams QoS guarantees a high-quality user experience by prioritizing and allocating network resources to audio, video, and screen sharing traffic. By implementing QoS, businesses can control bandwidth allocation and minimize performance degradation caused by network congestion.
How Does QoS Work?
QoS works by marking or “signing” packets to identify different applications, and then those markings are available at the different network devices along the route. Typically, you do this via the Operating System with some cooperation from the application. It involves settings IP fields and is typically organized by TCP/IP port by the OS and application.
For example, Microsoft offers guidance on how to configure and setup Microsoft Teams QoS markings. You can read about how to configure the markings via the Teams admin center: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoftteams/meetings-real-time-media-traffic.
Once the different packets coming from the Teams clients are set up, networks administrators configure downstream routers and apply policy for each of the applications (ports). And for this to be really successful, you have to do it for all the routers between the client OS machines and the network egress points. It can be a lot to organize, test, and validate with a network of reasonable complexity. Frequently, QoS breaks with the addition of new hardware or network device changes.
For Wi-Fi and access points, you must validate and test QoS signing. For access points to sufficiently support multiple in a Teams meeting sharing video and audio, or with Teams room functionality, the network can’t keep up without QoS and prioritization.
Prioritizing Microsoft Teams traffic will, for example, enable smoother online meetings and screen sharing while slowing down access from Minecraft or Fortnight on a LAN or across the WAN.
Initial Assessment and Best Practices
Consider these details when implementing QoS for Teams Monitoring
- Network Assessment
Before implementing Teams QoS, conduct a thorough network assessment to identify potential bandwidth limitations, latency issues, and bottlenecks. Understanding your network’s capabilities and limitations will allow for optimized Teams monitoring. - Traffic Classification and Prioritization
To effectively implement Teams QoS, it is essential to classify and prioritize Teams traffic according to its nature. Teams utilize several protocols for audio, video, and screen sharing, and each requires appropriate QoS settings. Ensure that you differentiate Teams of traffic and assign the appropriate priority levels, guaranteeing smooth communication. - Implementing QoS at the Edge
At the edge of your network, i.e., the point where your network connects to external entities, implement Teams QoS policies. This ensures that your organization’s Teams traffic receives priority treatment over non-essential traffic. Consider implementing features like Traffic Shaping and Traffic Policing to optimize network utilization and allocate bandwidth effectively. - Configuring QoS on Local Network
Within your local network, configure switches, routers, and firewalls to prioritize Teams traffic. Using Quality of Service mechanisms like Class of Service (CoS) or Differentiated Services (DiffServ) will grant Teams’s real-time media traffic the necessary priority. Implementing these mechanisms ensures smooth Teams communication, even during periods of high network congestion. - Monitoring QoS Enhancements
Implement a monitoring solution to track the effectiveness of your Teams QoS configuration. By monitoring various metrics, such as packet loss, jitter, latency, and throughput, you can identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments. Tools such as Exoprise Teams synthetics or Synthetic VoIP sensors can assist in assessing network performance and connectivity. - Troubleshooting QoS Issues
Despite careful planning and implementation, occasional issues may arise with Teams QoS. To troubleshoot such issues, monitor QoS-related logs and metrics, conduct packet captures, and utilize network monitoring tools. Analyzing these data sources will help identify and resolve issues promptly, ensuring optimal Teams performance. - Teams QoS Parameters
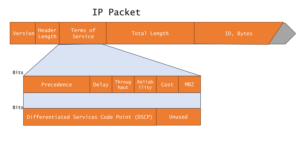
Teams QoS relies on two primary parameters: DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) and Expedited Forwarding (EF). Configuring these parameters at various network points, such as switches and routers, enables consistent prioritization of Teams traffic. In addition, prioritize voice and video traffic by assigning them lower latency.
The Importance of DSCP Configuration
Differentiated Services Code Point or DSCP is the first step towards optimizing Microsoft Teams traffic. Consider these important details regarding DSCP markings for Microsoft Teams:
- It is a field in the IP header that allows packets to be classified and prioritized based on different levels of service.
- With DSCP, Teams QoS enables real-time monitoring and management of network traffic, optimizing the performance of Teams calls and meetings.
- By assigning different DSCP values to various types of traffic, such as audio or video, administrators can prioritize important data, ensuring smoother communication experiences.
- Monitoring DSCP values in Teams QoS provides valuable insights into network performance, allowing administrators to identify and troubleshoot issues promptly.
- It allows for proactive management of the Teams environment, ensuring that network resources are efficiently utilized. Microsoft Teams Monitoring with DSCP ensures that organizations maintain high-quality voice and video calls, reducing latency and packet loss.
- Administrators can optimize network configuration, allocate bandwidth effectively, and prioritize traffic based on user needs.
- By leveraging DSCP for Teams QoS, organizations can deliver a seamless communication experience and enhance collaboration efficiency for their teams.
The Importance of Synthetic Transaction Monitoring for Microsoft Teams
So you want to prioritize Teams traffic to ensure optimal network performance for your end-users? You configure Teams clients to leverage DSCP markings but how do you know the impact on Teams latency, bandwidth, and packet loss? You can sit around and wait to see if users complain? Or wait weeks on end to see if the traffic or optimization has gotten better. Or, you can utilize a tool like Exoprise synthetics to generate Teams traffic without having to impact employees.
How Exoprise Enhances Teams Monitoring & QoS Implementation
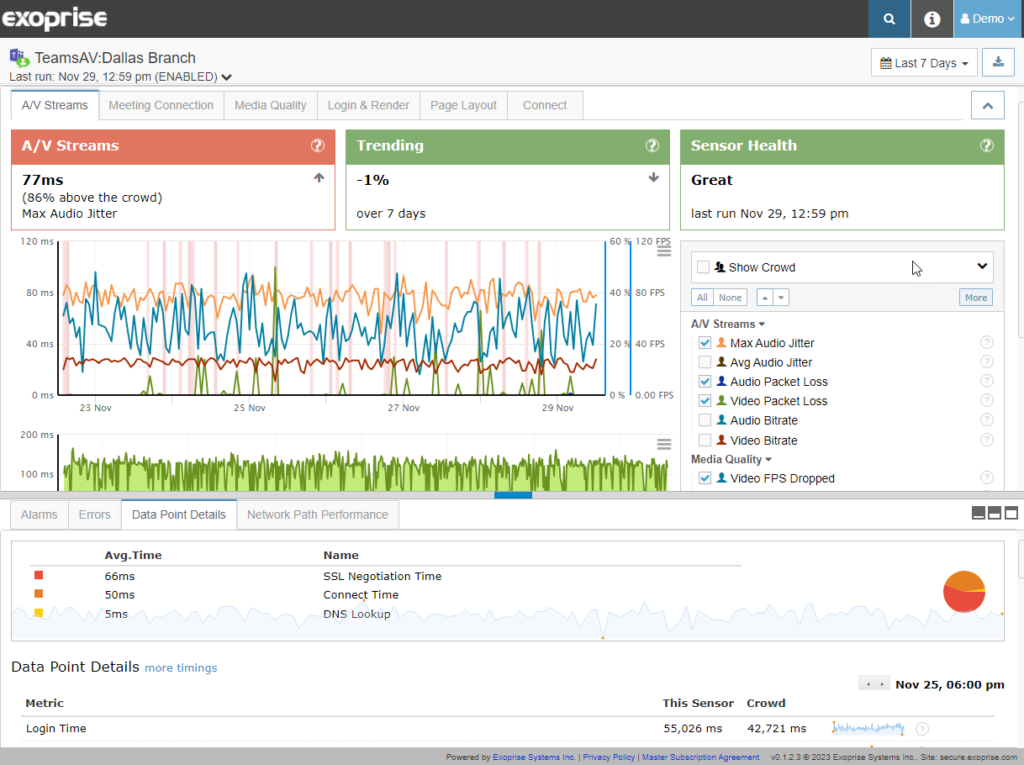
Exoprise offers Teams monitoring synthetics to provide continuous visibility and optimize the network for Microsoft Teams deployments. This monitoring tool executes synthetic video, audio, and messaging conference calls to assess the end-to-end Quality of Service (QoS) and WebRTC metrics. Additionally, with Exoprise Service Watch, by capturing the end-user perspective in real-time, it allows for easy diagnosis and troubleshooting before any issues affect the Microsoft Teams experience.
The monitoring tool provides rich insight into various metrics, including video and audio jitter, packet and frame loss, A/V error corrections, SSO, DNS, Connect, SSL timings, network congestion, bandwidth utilization, round-trip times to media servers, and network QoS. It can be deployed quickly, providing instant benchmarks compared to the CloudReady crowd, enabling businesses to see how their network performs.
With 24×7 synthetic audio, video, and messaging tests, businesses can ensure uptime and detect any network changes that may impact performance. The tool can be self-serviced and deployed to any branch or network topology, running alongside any workload, Windows device, or VM.
By correlating high-level metrics like Connect, Message, and Meeting Join Time with low-level QoS statistics such as jitter, frame, and packet loss, businesses can quickly identify and resolve LAN/WAN and SD-WAN problems. As Unified Communications and Collaboration (UCC) platforms like Microsoft Teams are critical to businesses, Exoprise’s monitoring tool helps isolate service disruptions, speeds up resolution time, and enables the creation of real-time call quality dashboards. Additionally, hop-by-hop Network Path Performance shows the bottlenecks in the Teams network path.
Merging QoS best practices and metrics with Exoprise Teams Monitoring solutions enhances the effectiveness of the QoS implementation process.
Conclusion
Implementing Teams Quality of Service (QoS) is crucial for organizations relying on Microsoft Teams for collaboration. Properly configuring QoS parameters, classifying and prioritizing Teams traffic, and monitoring network performance ensures high-quality audio, video, and screen sharing experiences.
Exoprise’s CloudReady Teams Monitoring tool is a comprehensive solution that optimizes Teams performance, meshing with QoS implementation. Synthetic testing evaluates end-to-end Quality of Service and WebRTC metrics, allowing for quick diagnosis and troubleshooting. This monitoring provides in-depth insights into network performance, allowing businesses to effectively configure QoS, then promptly address any issues and optimize the Teams experience.